必威betwayapp
毒品银行在线在你的指尖
必威国际app搜索我们的知识库的药物相互作用,药理学,化学结构,目标,代谢,和更多。下载有限的数据集,免费供学术和非商业研究人员使用。必威国际app

增强你的临床软件
整合我们的药物知识库与我们的临床药物数据API。使用灵活的数据模块,可以更快地进行规模使用和启动。为用户提供相关信息和先进的见解。

发现或重新利用药物
识别重新利用的机会,或构建预测性机器学习模型。我们结构化、广泛的数据集涵盖早期研究、临床试验和批准的药物。必威国际app
必威体育betway888交流群
- Fortamet
- Norvasc
- 奥美拉唑
- 特鲁瓦达Truvada的
特鲁瓦达是一种HIV核苷类似物逆转录酶抑制剂(HIV NRTI),已在美国、加拿大、意大利和欧盟等多个国家上市。它于2004年首次上市。它有口服药片,薄膜包衣,口服药片,包衣和口服药片。它含有两种活性成分:Emtricitabine和Tenofovir disoproxil,在其盐形式Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate。恩曲他滨是一种用于治疗和预防艾滋病毒的药物。替诺福韦二吡唑是一种用于治疗乙型肝炎感染和管理艾滋病毒感染的药物。
- 辛伐他汀
- 抗
Humira是一种肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)阻滞剂,在美国、加拿大、欧盟、意大利和印度尼西亚等多个国家都有销售。它于2002年首次上市。可采用皮下注射。它包含一种有效成分:Adalimumab。Adalimumab是一种用于治疗多种炎症性疾病的药物,如类风湿关节炎、克罗恩病和强直性脊柱炎。
- 赫赛汀
- Flonase
- b计划
- 易蒙停
易蒙停是一种非处方类阿片激动剂,在美国、加拿大、德国、哥伦比亚、意大利和印度尼西亚等多个国家均有销售。它于1983年首次上市。它有口服胶囊、口服药片和口服溶液三种。它含有一种活性成分:Loperamide,在其盐酸盐Loperamide形式。Loperamide是一种用于治疗腹泻的药物。
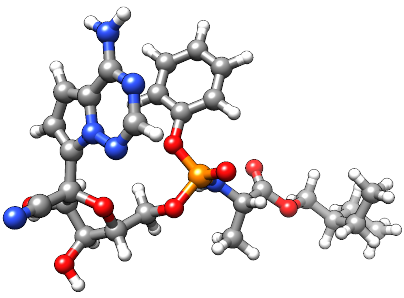
瑞德西韦
严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒2型(SARS-CoV-2)是2019冠状病毒病(COVID-19)的病原体,COVID-19是一种可发展为病毒性肺炎和急性呼吸窘迫综合征(ARDS)的呼吸系统疾病;COVID-19可能是致命的。与其他RNA病毒一样,SARS-CoV-2依赖于一种依赖RNA的RNA聚合酶(RdRp)酶复合物进行基因组复制,这种酶复合物可被称为核苷类似物的一类药物抑制。瑞德西韦(GS-5734)是一种三磷酸腺苷类似物,在2016年的文献中首次被描述为埃博拉的潜在治疗药物。[A191379, A222393]瑞德西韦的作用机制表明其具有广泛的抗病毒活性,迄今为止,它已证明对沙粒病毒科、黄病毒科、丝状病毒科、副粘病毒科、肺炎病毒科和冠状病毒科的体外抗病毒活性。2017年首次证明了瑞德西韦对冠状病毒科家族的活性,导致人们对瑞德西韦作为COVID-19可能的治疗药物产生了极大的兴趣。[A191427, A198810]瑞德西韦被证实为SARS-CoV-2及相关SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV RdRp的非专属链终止子,并在多个COVID-19临床试验中进行了研究。[L12174, L12177]根据汇总数据,瑞德西韦于2020年5月1日获得FDA紧急使用授权(EUA)。随后,FDA于2020年10月22日完全批准瑞德西韦作为COVID-19治疗药物,同时更新EUA,以覆盖未包括在批准适应症下的患者。Remdesivir目前在吉利德科学公司的商标名VEKLURY®下销售。瑞德西韦(Remdesivir)与baricitinib联合治疗COVID-19,于2020年11月19日获得FDA紧急使用授权。